Magazine, Past Issue
July/Aug 2025 issue
WHAT'S INSIDE: Screen-fast, sports betting, & environmental stewardship
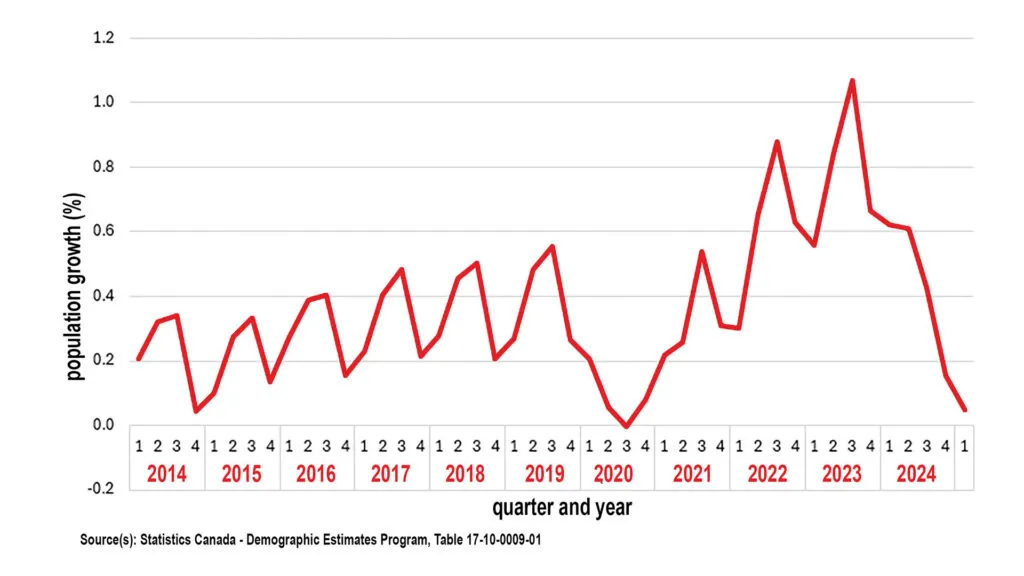
Our 10-day screen-fast challenge that we presented in the last issue is getting traction. Marty VanDriel has a story that shares how the fast went for him and others who gave it a try.
But that was just the start. Some generous supporters have recognized how important this issue is, so they are offering up a little extra motivation for us all. They have pledged to donate $100 to two fantastic kingdom causes – Word & Deed and Reformed Perspective – for every person who commits to and completes a 10-day fast from their screens from July 21 to 30 (to a maximum of $20,000 split between both causes).
Screens aren’t evil, but as the cover illustrates so well, screens can keep us from seeing reality – from seeing God’s loving hand upholding creation, this world, and our lives. Here now is your opportunity to join with some family and friends and maybe your whole church community to put screens aside and see the rest of the world unfiltered. Check out page 19 for more details or click on the QR code above to sign up.
Since sports betting was legalized in 2021, it has taken Canada by storm. If you watch any hockey you’ve noticed a lot of betting ads, and they bring with them a growing temptation for Christians to make some money while enjoying their favurite teams. But as Jeff Dykstra explains, we have good reason to steer clear of sports gambling.
In this issue we also do a deep dive into the topic of environmental stewardship by sitting down with two Christian women who work for an environmental group in the middle of a logging community in northern BC.
If you are an adult who tends to skip over the Come & Explore kids’ section, we encourage you to give this one a read. It will be sure to make you smile.
Click the cover to view in your browser
or click here to download the PDF (8 mb)
INDEX: Are you still able: A nation-wide challenge to experience life without screens / Creation stewards in a logging town / Who do you want to be? RP's 10-day screen-fast challenge / We took the no screens challenge... and now we're changing our habits / What can I do anyways? 35 screen-alternative ideas / Is TikTok the ultimate contraception? / How to stay sane in an overstimulated age / Defeated by distraction / How to use AI like a Christian boss / Who speeches were they? On AI, and others, writing for us / The Way / Who is Mark Carney? / What if we said what we mean? - the political party edition / Am I lazy or just relaxing? What does Proverbs say? / Get out of the game: Christians need to steer clear of sports gambling / Man up: ARPA leaderboards and the call to courageous action / Christians don't pray / Our forever home / Calvin as a comic / The best comics for kids / Fun is something you make: 11 times for family road trips / Come and Explore: Mr. Morose goes to the doctor / Rachel VanEgmond is exploring God's General Revelation / 642 Canadian babies were born alive and left to die / 90 pro-life MPs elected to parliament / Ontario shows why euthanasia "safeguards" can't work / RP's coming to a church near you

News
Saturday Selections – July 12, 2025
Josiah Queen's "A Garden in Manhattan"
On the crowded streets,
all the people that I see
Want them to know the Jesus that I know
If I'm the closest thing to a Bible that they read
Let the words they read be what You wrote
Father, help me to go
I'll be a garden in Manhattan,
be a river where it's dry
When my friends can't find the road,
I'll be a roadside welcome sign
Sunshine in Seattle,
be a cool breeze in July
Light in the darkness
I'll be a garden, a garden in Manhattan
Florida after dark,
I know it ain't quite Central Park
There's souls in my hometown You wanna reach
Oh, God, use me where You have me...
Climate hypocrisy tells us what the elites really believe
When global warming proponents like Oprah Winfrey, Bill Gates, and Jeff Bezos all jet off to an exotic locale to celebrate a wedding, you can know they aren't really worried about CO2 hurting the planet... or they wouldn't fly a hundred jets to a party. And as this article explains, EV cars are another hypocrisy gauge. They might make sense in some instances, but if they are being pushed whether they help lower CO2 emissions or not, then you know this is about show, not substance. As Bjorn Lomborg writes:
"In some parts of the world, like India, so much of the power comes from coal that electric cars end up emitting more CO₂ than gasoline cars...."
Now, to be fair, Lomborg himself is worried about global warming. But, as he highlights, the actions most governments take are not what would be needed to solve the issue if it did exist.
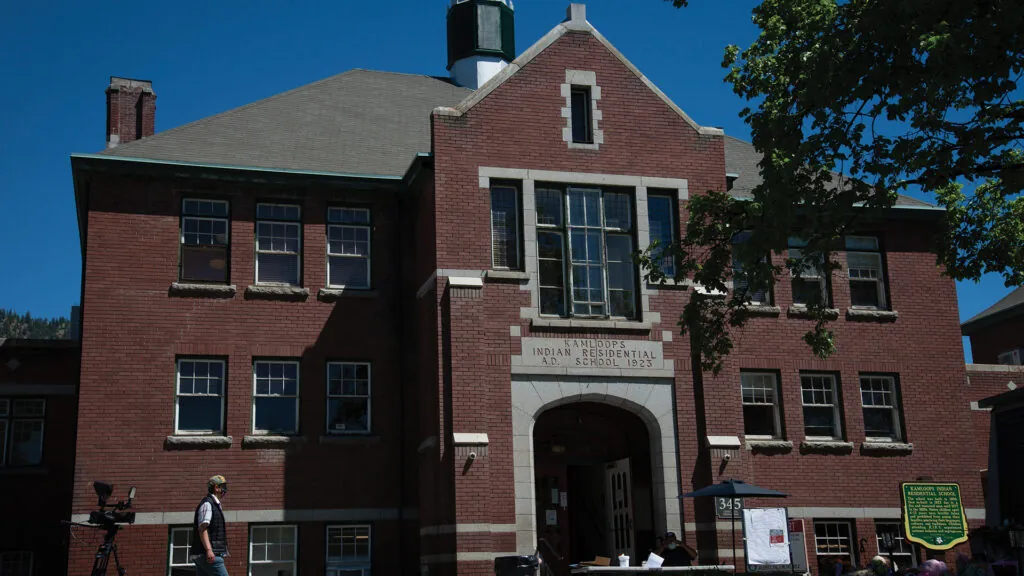
Parks Canada staff privately doubted Kamloops "graves" claim
“$12M spent by @GcIndigenous to find purported 215 children's graves at Indian Residential School was instead spent on publicists & consultants with no graves found to date...”
The legacy media is betraying Canada (10 min. read)
Soviet Union President Nikita Khrushchev is credited with saying, "The press is our chief ideological weapon." In contrast, US President George H.W. Bush is said to have said, "We need an independent media to hold people like me to account.” The dictator wanted to own the press so the government could use it to direct public opinion, while the US president touted the need for a press independent of government so it could hold those in power to account.
Our Canadian government spends massive amounts of money funding the country's largest media outlets, and these outlets not only don't denounce the proposition, but take the money. That tells you a lot about which direction our media is heading.
While readers likely won't mind this article's anti-Liberal Party bias, some might be put off by just how loud it is. But read it anyways for the money trail.
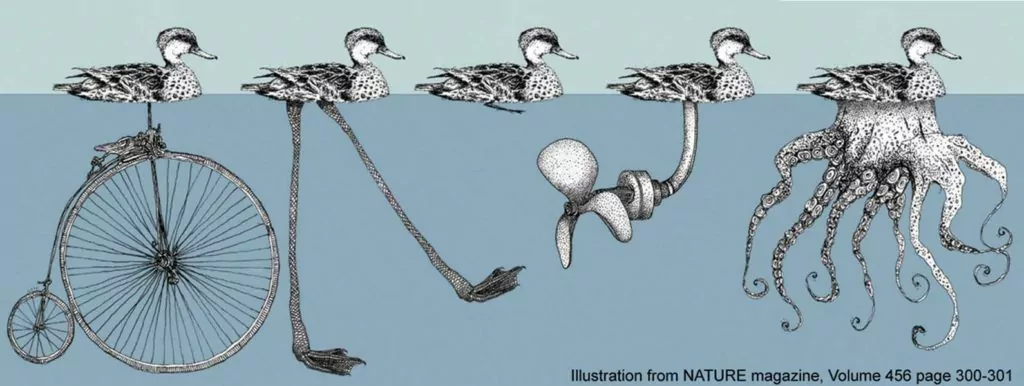
The Scopes Monkey Trial is 100 years old!
In 1925, a Dayton, Tennessee high school teacher named John Scopes was put on trial for violating a state law that forbade teaching evolution. The case made big news then – across both the US and into Canada – and made big news again in 1960 when a movie version called Inherit the Wind was made, which portrayed the town of Dayton as a bunch of creationist hicks who wanted to storm the jail to get Scopes. That film was then shown in classrooms across the US for generations, convincing many students that only idiots like those onscreen could ever believe Genesis is literal.
But the truth is, the whole town was in on it – they challenged the law to get some attention for their hometown, and recruited Scopes, who agreed to be charged, and in an ironic twist, he probably never even taught evolution in his classroom. In another ironic twist, as this article lays out, much of the scientific evidence marshaled for evolution during the trial has been overturned since (ex. vestigial organs, similar embryonic development). So, even if it had been a bunch of dumb hicks, dumb hicks siding with God are a lot smarter than a gaggle of reporters and scientists siding against Him.
Is Trump doing good or is he doing bad? Yes.
Jeffrey Epstein was a sex trafficker with ties to many of the most powerful people in the world. This, then, was a man who could name names, and topple empires... and then he died mysteriously in his jail cell – a purported suicide but one that happened when his cell's video cameras were broken. The country's reaction was telling. No one was buying the coincidence. This past week, Epstein's client list was supposed to be released and the news now is that there was no client list. As the video below details, this has a lot of conservatives, Christians among them, feeling crushed. They don't believe it, and want to know where the justice is.
Part of the disappointment comes from the tendency we have of making politicians our dividing lines. Joe Biden and Kamala Harris were monsters... so we should love Trump? That doesn't follow. Canadian prime ministers Trudeau and Carney have a litany of sins, most recently trying to push murder as a treatment for mental illness. But does that mean we have to look past the shortcomings of Pierre Poilievre? Christians don't have to. Our dividing line is not a Trudeau or Trump, because our unswerving loyalty lies only with God (Josh. 5:13-14). So, yes, Trump continues to stand strong against gender nonsense, but the missing Epstein list has people wondering if the swamp can ever be drained, and as Mindy Belz (sister-in-law of WORLD magazine founder Joel Belz) highlights, his results-now approach has undercut processes that protect everyone from government overreach.
Today's Devotional

July 13 - Calling the Sabbath a delight
“If…you call the Sabbath a delight….Then you shall delight in the Lord.” - Isaiah 58:13,14
Scripture reading: Isaiah 58:1-14
Isaiah 58:13-14 is a wonderful passage to reflect on as we prepare to go to the house of the Lord for worship on this Sabbath day. Notice clearly the if/then structure of these verses. The Lord is telling us that if we call the Sabbath >
Today's Manna Podcast

Redemption: In His Presence
Serving #902 of Manna, prepared by D. VandeBurgt, is called "Redemption" (In His Presence).