by Marcos Eberlin
2019 / 147 pages
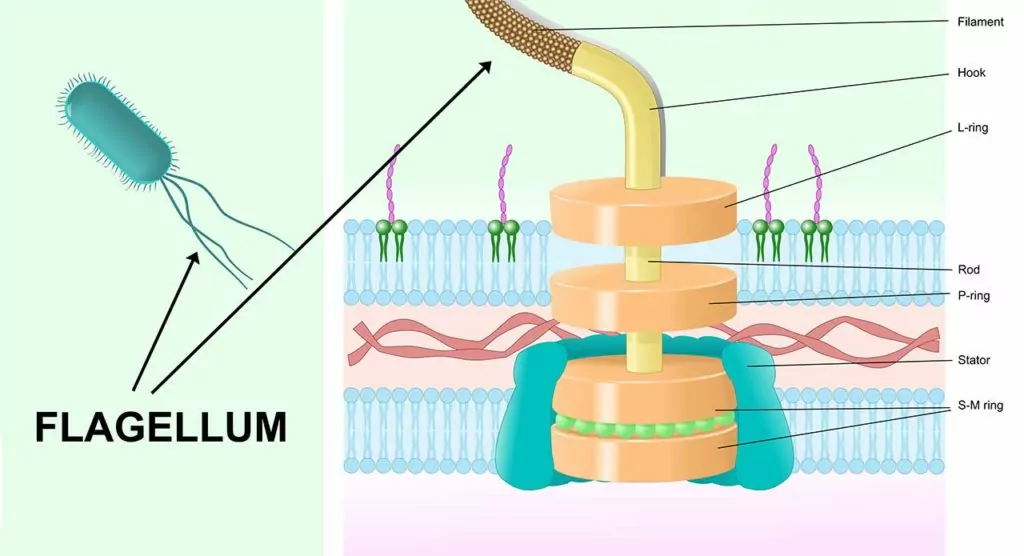
Back in 1996 “Irreducible complexity” was Michael Behe‘s contribution to the origins debate: he argued that some biological structures couldn’t possibly have evolved because there is no way they could have come about by evolution’s stepwise-process – the complexity of micro-machines like a bacteria’s flagellum motor was irreducible.
Now Marcos Eberlin is making a similar point, but bringing a new piece of rhetorical ammunition to the fight with Foresight in which he argues the deeper we delve into the biological world the more we discover “artful solutions to major engineering challenges.” These solutions, he explains, look to “require something that matter alone lacks…. – foresight.”
With this term “foresight,” Eberlin is arguing some biological abilities couldn’t have come about as a response, but had to be the result of anticipation. So, for example, cells, right from the beginning, had to anticipate the problems that would come with using oxygen:
The oxygen (O2) molecule is essential to life, but only a life form that can efficiently wrap and transport the devil O2 exactly to a place where it can be used as an energy source would benefit from its angel side. Otherwise, O2 becomes life’s greatest enemy.
Rupture the membrane of a living cell, exposing it to the air, and you will see the great damage O2 and a myriad of other chemical invaders can do to a perforated cell. Death would be swift and sure. From an engineering standpoint, then, it was essential that a way is found to protect the cell, life’s most basic unit. The solution was clever: The cell was surrounded by a strong chemical shield, from the very beginning.
It is often said that a solution always brings with it two additional problems, and a cellular membrane shield is no exception. A simple shield could indeed protect the cell interior from deadly invaders, but such a barrier would also prevent cell nutrients from reaching the inside of the cell, and it would trap cellular waste within. Small neutral molecules could pass through the membrane, but not larger and normally electrically charged biomolecules. A simple shield would be a recipe for swift, sure death. For early cells to survive and reproduce, something more sophisticated was needed. Selective channels through these early cell membranes had to be in place right from the start. Cells today come with just such doorways…
…..a gradual step-by-step evolutionary process over many generations seems to have no chance of building such wonders since there apparently can’t be many generations of a cell, or even one generation until these channels are up and running. No channels, no cellular life. So then, the key question is: How could the first cells acquire proper membranes and co-evolve the protein channels needed to overcome the permeability problem? Even some committed evolutionists have confessed the great difficulty here. As Sheref Mansy and his colleagues put it in the journal Nature, “The strong barrier function of membranes has made it difficult to understand the origin of cellular life.”
So Eberlin concludes: “There would be no hope for a cell to become viable if it had to tinker around with mutations over thousands of generations in search of a functional membrane. It’s anticipate or die.”
This is but his first example – Eberlin is arguing that wherever we look at life, “the evidence of foresight is abundant.” That’s true in the fine-tuning of the universe, where gravity had to be just so, Earth had to be just the right distance from the Sun, and had to have enough water, and water needed to have certain specific properties. Oh, and the planet needed to have just the right amount of lightning too.
That foresight is also evident in the structure of our DNA – which has to be stable – and RNA – which has to be malleable.
He goes on and on, diving into these examples, and showing how brilliantly problems have been anticipated and solved. But by who? Well, Eberlin doesn’t really get into that until the final chapter, and it is in the book’s very last line that he gives credit where it is due: “Great are the works of the Lord.”
I loved this whole book, but will confess to only understanding about two-thirds of it clearly. But even when it got more technical, the gist I did catch was still utterly fascinating. I’d recommend it to anyone with an interest and at least some high school science.