Magazine, Past Issue
May/June 2025 issue
WHAT'S INSIDE: If businesses tithed / Pierre Poilievre: sometimes access comes with too high a cost / Being thrifty and finding hope / A principled (and practical) guide to tithing / 5 things I'd like my kids to learn about money / God love a cheerful giver: 6 ways to restore the joy of giving / How to lock your phone from pornography... 101 / A Church response is needed to stop the porn crisis / RP's 10-day screen-fast challenge / Signing on the dotted line? A creative approach to boundaries in dating / Becoming Chinada? - a look at our country, from the eyes of a recently arrived Chinese family / Books: education littles will love (including "5 on our feathered friends") / 7,000 pages in, and now this? Another popular series, Keepers of the Lost Cities, takes a turn... in book 11 / Write down your story: sharing your history is sharing His history / What kind of Prime Minister could he still be? 5 things you might not have known about Pierre Poilievre / Upheld: a widow's story of love, grief & the constancy of God / Morning and Evening: a teen offers up a different sort of book review for Spurgeon's classic devotional / 3 on comforting suffering Christians / Stockholm Syndrome Christianity / Get to know John Calvin / Christian films for families / Come and Explore: Bald Eagle / Don't follow your heart / A word for a new mother... as given at her first baby shower / Our family's trip to the Ark / Ruth de Vos is quilting kids and creation / Wise and Innocent / Coming soon: RP's merch store! / and more!
Click the cover to view in your browser
or click here to download the PDF (7 mb)

News
Saturday Selections – May 3, 2025
Be Present
Reformed rapper Propaganda with a message that'll hit everyone hard:
"I guess you could say I've been through a divorce now – me and my phone are no longer married."
p.s. "finna" means "going to"
An encouraging message for Canadian Christians after election night
The same God who promises to turn everything to our good (Romans 8:28) was sovereignly in control when Mark Carney got voted in. So we know this is right, and to our benefit, even if we don't understand... at least in full.
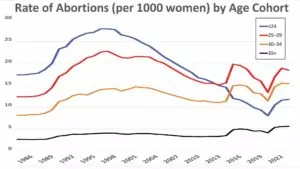
One possible benefit – an evident silver lining – is the 90 pro-life MPs that RightNow says were elected. Pro-life candidates are banned from the NDP and Liberals, so these must all be Conservative, and 90 out of the 144 elected Conservatives is quite the sizeable segment. And being in opposition can be freeing, as it may allow these MPs to speak against government abuses more openly than they'd ever be allowed if they were government. Maybe some will start talking about the unborn, not just to fellow pro-lifers, but to the muddled middle who might yet be convicted of the wickedness of this slaughter.
Encouraging coverage of ARPA Canada
This week ARPA Canada got to make a presentation in the BC legislature with around 20 MLAs present, and this mainstream media account covered it straight up.
Want to improve your life?
"Open the Bible at least four times a week."
Stop valorizing doubt! (10-minute read)
As Trevin Wax notes, "Honesty about our doubt is a virtue, but it’s the honesty that’s commendable, not the doubt itself."
Syncretism is a pressing temptation
As Pastor John Van Eek notes in the video below, syncretism is the mixing of any two (or more religions) to form a completely new religion. Or to put it another way, Christianity plus anything isn't Christianity anymore.
In the past God's people might have mixed their true religion with Baal worship, but today's syncretistic temptation involves a very different religion: secularism. In the public square, the demand is that Christians limit ourselves to sharing a logical, scientific, or maybe "common sense" perspective, but never an explicitly Christian one. Now, Christianity is logical, and lines up with science (when properly understood) so this might seem a demand we could accommodate.
But when we understand that the secularism making these demands holds that man's reasoning is the source of all knowledge, including what is good, right, and meaningful, then we can see how secularism is another religion. And then we can also start to see the syncretistic element here. If Christians agree to act and argue as secularists do – with no mention of the God we were created to glorify (WSC Q&A 1) – then even when we are pursuing good ends, like fighting a trans agenda or trying to stop abortion, we are doing so by mixing secularism with our Christianity.
And then is that Christianity still?
Today's Devotional

May 8 - An unbreakable covenant
“While the earth remains, seed time and harvest, cold and heat, summer and winter, day and night, shall not cease.” - Genesis 8:22
Scripture reading: Jeremiah 33:14-26; 2 Peter 3:8-13
Many “experts” predict that the world will end due to a great calamity from climate change or a meteor striking the earth. But the Lord assures us that the sun will rise and set >
Today's Manna Podcast

The Enduring Word of God
Serving #836 of Manna, prepared by Greg Bylsma, is called "The Enduring Word of God".