It all starts with an invitation from the Grade Twelve English teacher, Tom Van Swift, to come and enjoy the final field trip of the year, just before graduation. When the students meet in the school foyer at the beginning of the school day, Mr. Van Swift tells them to take the elevator to the second floor.
When the seven students, along with Mr. Van Swift, arrive at the second floor, they find the room (which should be the library) to be pitch-dark.
“Where are we?” asks Adam.
Mr. Van Swift answers, “I made a few minor modifications to the elevator. You’re now in some other dimension – of sight, of sound, of mind.”
The track star of the bunch, Barbara, replies with a wit just as quick as her feet, “It’s a little too dark in here for The Twilight Zone. Can we please get some light?”
“Lights… and action”
So, Mr. Van Swift calls, “Lights… and action,” and that is the last the class sees or hears of him for some time. What they do see, in fact what they are standing on, is the battlements of a medieval castle, in the dying light of early evening. They themselves are dressed in Elizabethan clothes, and the man standing before them looks very familiar…
“Hey, wait a minute, you’re William Shakespeare!” exclaims Cedric.
“Yeah,” says Isaac, and adds, “and this is a re-creation of one of your plays. Hamlet, right? ”
Suddenly, Johanna speculates, “Is this, like, a time machine?”
“Forsooth, forsooth,” laughs Shakespeare. “Hinder me not, and I will repay your queries with what wit I can muster, in proper order. First, I am indeed the Bard of Avon, William Shakespeare. And this is – as you have truly divined – what you call a… re-creation of part of my own favorite play, Hamlet. Howe’er, as to whether this is a… time machine, I know not what thou dost speak of.”
“Well, that’s a little hard to explain,” says Muriel. “But… why are we here?”
“Fairly asked, young maiden, and ’twill be fairly answered,” says Shakespeare. “Over the centuries that my plays have been performed – and studied – in your schools, I have oft heard complaint and protest (methinks, too much) over the ending of my favorite play. It seems that people, especially students, bewail the death of my sweet prince Hamlet as much as I often do.”
“Yeah, why should he die?” asks Oliver, who played the Emperor in the school production of The Emperor’s New Clothes. “My character’s vanity was a tragic flaw, just like Hamlet had… but he didn’t die from it.”
“Aye, but your play was a comedy, was it not?” counters Shakespeare. “In a tragedy, as oft in the real world, life must, alas, be lost when once we leave law’s limits. There is a way to save my Hamlet, but first let us scan this closely: What brings Hamlet headlong to his deadly destiny?”
“Well, some say Hamlet’s weakness was indecision,” rejoins Oliver confidently, “but Mr. Van Swift says that he read a Christian book that said his real flaw was being too vengeful.”
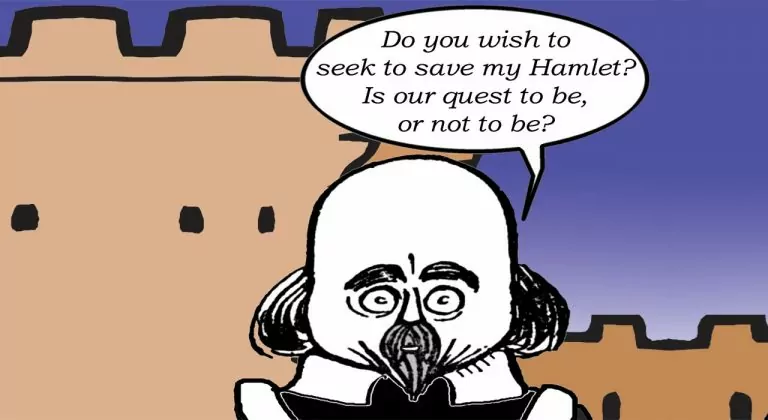
“Well, if what thou sayest be truth,” Shakespeare replies, “it is certainly clear that vengefulness deserveth death. Still, do you wish to seek to save my Hamlet? Is our quest to be, or not to be?”
Muriel hesitantly answers, “To be, I guess. What do we need to do?”
Shakespeare explains, “Paint for me how my Hamlet was too vengeful.”
“I think I know,” replies Johanna. “Is it partly that he resents his uncle Claudius for getting married to his mother so soon after his father’s death? That makes Hamlet only too ready to believe that Claudius poisoned his father for his throne, right?”
“Yeah, that’s right,” says Isaac. “And then Hamlet doesn’t accuse his uncle publicly, but starts acting like he’s some kind of private eye.”
“Yeah, and he doesn’t even tell his best friend what he’s thinking, but goes on a personal vendetta against Claudius and his servants,” says Barbara, who also quickly accuses Hamlet of fleeting love toward his girlfriend: “He even treats Ophelia badly ’cause he thinks all women are like his mother – disloyal to their true love.”
“Don’t forget that Hamlet won’t kill Claudius when he thinks Claudius is praying, because he wants to send his uncle not just to death, but to hell. Now that’s vengeful!” concludes Adam.
“And thou hast not even mentioned that Hamlet hath innocent blood on his hands, either by mistake or by malice, when he killeth Polonius, Rosencrantz, and Guildenstern,” says Shakespeare, “because he believeth they are working with Claudius against him.”
“I know,” says Mr. Van Swift finally, stepping out from behind a pillar. “And this battlement is where it all starts, when Hamlet sees his father’s ghost on a moonless night just like this one. But now, how about changing the ending?”
“Well, as I wrote the ending,” Shakespeare replies, “Hamlet dieth when Laertes, the son of the old man Hamlet killed, stabs Hamlet with a poisoned sword in a fencing competition arranged by Hamlet’s uncle Claudius.”
“We know that,” says Mr. Van Swift. “However, because this is not a time machine, but a mind machine, you simply have to rewrite this original manuscript I just found in my hand, with this quill pen I just found in my front shirt pocket, and the ending of every copy of Hamlet in the world will be changed.”
“O brave new world, that hath such cunning wonders in it,” says Shakespeare. “There is only one way in which thou hast overleaped thyself, Mr. Van Swift. My play is, and should be, a tragedy. If Hamlet doth not die for his tragic flaw, then someone else must die willingly in his place.”
Startled, the class hears Mr. Van Swift say casually, “So write somebody in to step in the way of the poisoned blade. How about that pompous Osric guy?”
“But, Mr. Van Swift,” pleads Shakespeare, “how can I ask one of my characters to die willingly for the sins of another? That is not right. Besides, Osric has his own faults to be punished for. He cannot stand in for another. No, there is only one person who can save Hamlet – his maker… me.”
A quick rewrite
Now it is Mr. Van Swift’s turn to be dumbstruck. “You? You’re willing to die for Hamlet? But you’re a person, created in God’s image. He’s only a character.”
“Be not so hasty in thy reasoning. The person of Shakespeare is not in peril. My soul is not here. Its destiny rests in God’s hands. What I would lose is my reputation, my glory. If I write myself into the script to save Hamlet, the name of Shakespeare will disappear. No-one will ever again know who really wrote Hamlet or Midsummer Night’s Dream or any of my more than thirty other plays. In fact, no-one will even know whether or not all my anonymous plays were written by the same person. In the public mind, my sweet prince Hamlet will live on, as he should, but Shakespeare will vanish.”
Mr. Van Swift is paralyzed in horror as Shakespeare takes the manuscript and quill and begins to insert some lines for a character named… William of Avon… who overhears Claudius’s plot; is captured; escapes; and at the last minute warns Hamlet, but is stabbed by the poisoned sword himself. Even as Shakespeare writes, his features change. His face grows younger, more like his earlier actor self. Then he begins to fade as the scene in the mind machine changes to a royal palace in the middle of a fencing match between Hamlet and Laertes, with a roaring fireplace at one end of the room, and the rewritten manuscript lying near it. The class sees a new character, a sort of young-looking Shakespeare, rushing in to warn Hamlet. Just before “William of Avon” can step in between Hamlet and his opponent, Mr. Van Swift screams, “No!” and hurls the rewritten manuscript into the blaze in the fireplace. The flames seem to fill the room for a moment, and everyone’s eyes close against the glare.
The last act
When the students open their eyes, they are back on the castle walls, with the “old” Shakespeare chuckling as he rebukes their teacher: “Really, Mr. Van Swift, I hope thou hast learned something from all thy meddling with literature. Art thou not a Christian? Yet thou art shocked when I am willing to treat one of my sinful characters, whom I had made, as a friend. Doth not God do the same for His people? Jesus said, ‘I no longer call you servants, but friends.’”
“Yes, but to have Shakespeare’s name disappear!” says Mr. Van Swift. “It’s unthinkable! There is glory and majesty in that name!”
“The Son of God had far greater glory and majesty,” counters Shakespeare, “but He did not count His equality with His Father as something to be greedily held on to. Rather, He gave up His glory and humbled Himself unto death. He was willing to step into the story He had written as one of the Persons of the Tri-une God, rather than let it simply perish in the flames – as you were only too willing to let happen.”
“But what good is all this to our Grade Twelve students?” replies Mr. Van Swift. “I was trying to show them how they have the power to change things, and you’ve just shown them that everything stays the same.”
“Actually, Mr. Van Swift, thou shewest them that when thou did not let me change the play. However, thou also revealed what a great and terrible thing it is for the Maker to step into His own story. Meditate upon that for a while, as thou ponderest also how to respond to the love of the Divine Storyteller.”
“This all reminds me,” says Mr. Van Swift, slowly, “of Philippians 2. One way to respond to a God who steps into His own story is ‘with fear and trembling,’ as we ‘work out’ the roles he has set for us in the story He has written for us.”
“Now that, forsooth, is an ending worth keeping,” says Shakespeare, as both he and the castle begin to fade. “Remember me,” he says faintly, with a ghostly grin, as the students find themselves in their own school library.
“So, class,” says Mr. Van Swift. “Not what I meant to teach, but remember this as you graduate from our school. God the Son, who with God the Father and the Spirit is our Maker, gave up His glory and stepped into His story to save us, calls us His friends, and now enables us to carry out, with fear and trembling, the parts He has given us, in His–Story.”
Jeff Dykstra admits that C. S. Lewis thought of making Shakespeare a character in his own play first – as a symbol for the Incarnation. However, Jeff wrote it as a story first.