Politics
Man Up: ARPA leaderboards and the call to courageous action
We live in a time of deep confusion about truth, morality, identity, and even the basic purpose of life. Many young people today are unanchored, unsure of what faithfulness looks like in the world around them. As Francis Schaeffer noted, “Modern man has both feet firmly planted in mid-air.” But following Christ is not just about holding the right beliefs in private. It means living those beliefs out boldly, in public, and without compromise.
God calls His people to bear witness to the truth in every sphere of life, including the political realm, where laws are made, values are shaped, and the vulnerable are either protected or ignored. Young people are not exempt from this calling. Scripture gives us examples like Daniel in Babylon, David facing Goliath, and Timothy in the early church – young men who stood firm in the face of pressure, hostility, or fear.
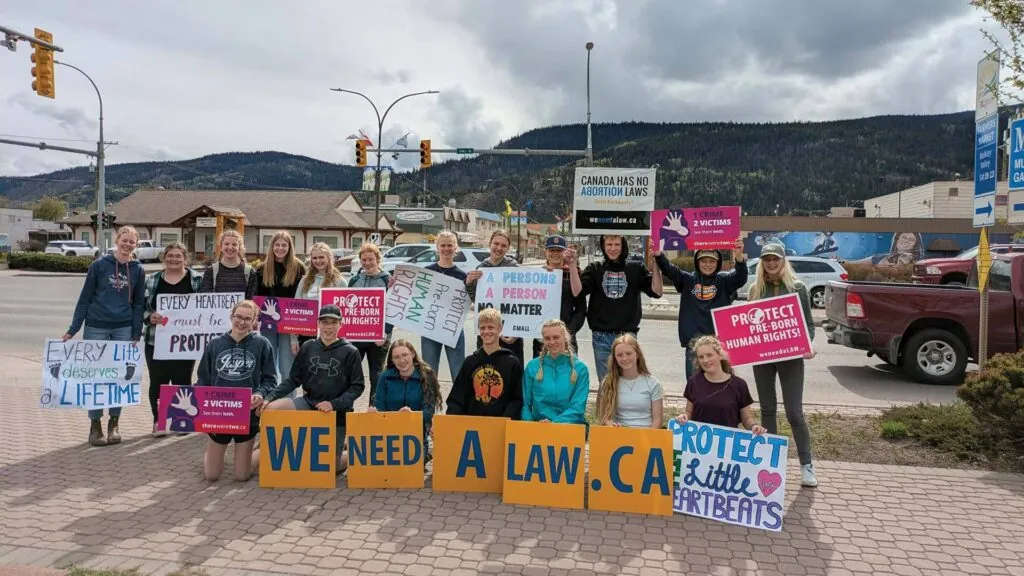
That same spirit of faithful action is exactly what ARPA’s Leaderboards competition aims to cultivate. Over the past school year, students across Canada have stepped up by writing letters, hosting events, engaging with elected officials, and standing for life and truth in their communities. Their efforts are a reminder that Christian youth can be courageous, creative, and committed to something far greater than themselves.
This article highlights what they did and why it matters. In particular, it takes note of a striking feature from this year’s competition: the individual winners at the top of the Leaderboard were all young men. In a culture where male leadership is often dismissed or diminished, that’s worth celebrating. More than that, it invites us to consider what godly leadership actually looks like, and how we can raise up the next generation to embrace it.
What is ARPA Leaderboards?
 All sorts of ways to be active, and earn your ARPA club points.
All sorts of ways to be active, and earn your ARPA club points.
ARPA Leaderboards is a national student competition that turns political action into a hands-on, community-based challenge. It’s designed to encourage Reformed high school and homeschool students to bring a Christian witness into the public square, and not just in theory, but in practice.
Throughout the school year, students form ARPA clubs – these are usually based in Christian schools or homeschool co-ops – and then choose real-world political or cultural actions to carry out together. These actions include things like organizing pro-life flag displays, writing letters to MPs or editors, meeting with local representatives, collecting donations for pregnancy care centers, or educating others through public events. Each completed action earns points, and photos and reports are posted on the Leaderboards website. There are prizes both for individual students and for school clubs, but the real reward is learning how to serve Christ with courage and clarity in public life.
While Leaderboards encourages competition, its deeper goal is to encourage young people to take initiative and speak with clarity in the public square. By combining teamwork, creativity, and accountability, it helps young people gain confidence and conviction as they speak out on issues of justice, life, and truth. And it makes political engagement less abstract – less something “for us as adults later” – and more of a concrete expression of public obedience to Christ here and now.
 Immanuel Christian School students singing at an old age home.
Immanuel Christian School students singing at an old age home.
Highlights from this year
From September to May, students across the country took action that was thoughtful, bold, and often outside their comfort zone. What began for many at an ARPA Youth Conference (where they learned about pro-life advocacy, wrote postcards, and distributed flyers), soon turned into a steady stream of public witness in their own communities.
One of the most visible efforts was the all-pink flag display in Burlington, Ontario, drawing attention to the injustice of sex-selective abortion. Students from TEACH Home Educators of Brant and Emmanuel Christian High School of Fergus came out to plant flags, engage with passersby, and take down the display afterward. Emmanuel Christian High School went on to host not one but four flag displays throughout the year!
Some actions were deeply relational. Several clubs, including Immanuel Christian School of Winnipeg, organized visits to seniors’ homes, singing, encouraging, and reminding elderly residents of their value and dignity in Christ. Others gathered resources for local pregnancy care centers or raised funds through school-wide initiatives.
 Emmanuel Christian High School students meeting with their local Member of Parliament
Emmanuel Christian High School students meeting with their local Member of Parliament
Some students stepped into more direct engagement with public officials. Emmanuel Christian High School met with both their Member of Parliament and newly elected Member of Provincial Parliament to talk about key issues. Mia Vandermaarel of TEACH Home Educators of Brant wrote letters to the editor that were published in the Toronto Sun, Winnipeg Sun, and Hamilton Spectator, helping shape public conversation from a Christian perspective.
Many clubs also came up with entirely original projects. One group from Coaldale Christian School hosted a student-led apologetics night, where students taught their parents the basics of pro-life argumentation… and even cooked dinner for them! Another group, involved in ARPA’s Let Kids Be campaign, set up a roadside sign warning about the harms of gender transition for minors. When the sign was vandalized, students from Ebenezer Canadian Reformed School returned late at night to repair and re-install it.
Not every action was large-scale, but each one mattered. Students wrote pro-life messages with sidewalk chalk for people to see along public pathways. Others knit baby hats (each one representing a life lost to abortion) and sent them to Parliament. Stickers with clear, hopeful pro-life messages appeared on cars, lockers, and backpacks.
Taken together, these efforts showed that faithfulness isn’t about age, comfort, or platform. It’s about showing up, speaking out, and putting your beliefs into action – even when no one is watching.
 The men on the Leaderboard
The men on the Leaderboard
“The world cries for men who are strong: strong in conviction, strong to lead, to stand, to suffer.” – Elisabeth Elliot
One of the most striking details from this year’s competition was the individual leaderboard. At the top were three young men: Evan Roth, James Thalen, and Asher Vandermaarel. These weren’t just occasional contributors; they were consistent, committed, and quietly courageous.
Evan registered for an ARPA Youth Conference in the fall, participated in the March for Life, visited an old age home, handed out Let Kids Be flyers, and used sidewalk chalk to spread the We Need a Law message. He also wrote postcards to MPs and MLAs, took part in several flag displays, and repeated most of these actions more than once. James and Asher took on similar efforts, showing the same kind of persistence and dedication over the course of the school year.
In a time when male leadership is often absent or dismissed, these young men modeled something countercultural: initiative, responsibility, and public conviction rooted in their Christian faith. They didn’t act alone. Like most students in the Leaderboards program, they had guidance from a teacher or club leader, and encouragement from the ARPA staff along the way. But what set them apart was their willingness to take initiative. They followed through, again and again, often going beyond what was expected. They acted faithfully, consistently, and with conviction, because they believed it mattered.
This kind of leadership matters. In many of our churches, we’re seeing fewer men entering the ministry and fewer desiring to serve as elders and deacons. And while ARPA’s local adult chapters across the country continue to thrive, many still see greater involvement from women than men. That’s not cause for despair, but it is a reminder of how valuable it is to see young men stepping into public responsibility with clarity and courage.
Evan, James, and Asher are reminders that faithfulness doesn’t require a title or a platform. It requires conviction, courage, and the willingness to be counted.
A brief biblical case for male leadership in public life
 Ebenezer Canadian Reformed School students getting the message out with a ”Let Kids Be” sign.
Ebenezer Canadian Reformed School students getting the message out with a ”Let Kids Be” sign.
The Bible presents a consistent pattern: men are called to take initiative, accept responsibility, and lead with humility and courage – not just in the home and church, but also in the broader public realm. From the beginning, Adam was placed in the garden to “tend and keep it” (Gen. 2:15), a charge that includes cultivation, guardianship, and stewardship. That calling – to bear responsibility for the world God made – echoes throughout redemptive history.
Again and again, we see God raising up men to stand in the public square and confront injustice, call rulers to account, and proclaim His truth:
- Moses stood before Pharaoh, not merely asking for Israel’s release, but declaring the sovereign rule of God over kings: “Thus says the Lord God of Israel: ‘Let My people go’” (Ex. 5:1).
- Nathan confronted King David after his sin against Uriah and Bathsheba, saying, “You are the man!” (2 Sam. 12:7), a courageous act of public accountability.
- Elijah boldly rebuked Ahab for Naboth’s murder and Israel’s idolatry (1 Kings 21).
- Isaiah stood before kings like Ahaz and Hezekiah, urging trust in the Lord rather than foreign alliances (Is. 7; 37–39).
- Jeremiah warned Zedekiah and the officials of Judah, saying, “O house of David! Thus says the Lord: ‘Execute judgment in the morning…’” (Jer. 21:12), even as he was imprisoned and persecuted for his message.
- Amos condemned Israel’s ruling class: “They hate the one who rebukes in the gate, and they abhor the one who speaks uprightly” (Amos 5:10), calling out systemic injustice.
- Micah declared, “Hear now, O heads of Jacob, and you rulers of the house of Israel… who hate good and love evil” (Micah 3:1–2), directly confronting civic corruption.
- Daniel, serving under pagan kings, boldly interpreted dreams and declared divine judgment: “You have been weighed in the balances, and found wanting” (Dan. 5:27).
These men were not grasping for personal gain or prestige. They bore public responsibility because they feared God more than man. Whether they held office or spoke prophetically to those who did, they understood that political power is not evil in itself – it is a tool to be used in submission to God’s authority and for the good of others. They spoke with clarity, even when it cost them dearly.
The New Testament carries this same vision of principled courage. Paul exhorts believers: “Watch, stand fast in the faith, be brave, be strong” (1 Cor. 16:13). Though the church is not a political body, it is called to form men who will lead well in every sphere of life, including the public square.
This is not a call to control others or seek power for its own sake, but to take initiative with conviction, courage, and a willingness to bear responsibility for the good of others.
What we saw this year in the Leaderboards competition was a glimpse of that calling. In a time when many young men are uncertain about their role or place, we saw a few step forward – not perfectly, but faithfully. And that is something to thank God for, and to build on.
 Speaking truth at the Toronto March for Life.
Speaking truth at the Toronto March for Life.
More than politics: preparing for lifelong engagement
Leaderboards isn’t just about winning a prize or checking off action items. It’s about planting the seeds of long-term involvement – helping students gain the confidence, skills, and motivation to be engaged Christian citizens well into adulthood.
We often hear from ARPA chapter leaders that they wish more men were actively involved. That gap doesn’t close by accident. It closes when young people are shown early that political action is a normal and necessary part of Christian responsibility. Leaderboards helps do exactly that. It gives students a framework for understanding the issues and a place to start acting on them.
The hope isn’t just that they participate for a season. It’s that they carry these habits into the rest of their lives by joining ARPA chapters, meeting with elected officials, and encouraging others in their church community to speak up. If we want faithful, engaged adults tomorrow, we need to invest in opportunities for them to participate today.
That’s the kind of momentum we want to carry forward – not just into next year’s competition, but into a lifetime of public faithfulness.
The work isn’t finished
This year’s Leaderboards competition gave us a glimpse of what’s possible when young Christians take action. Some wrote letters. Others planted flags. A few stood in front of MPs or in front of their entire school. And at the top of the individual leaderboard, a handful of young men took initiative, showing maturity, discipline, and a willingness to lead.
But this isn’t just about one season or a few standout students. It’s about what comes next.
Canada doesn’t just need more political activity. It needs principled, faithful leadership – rooted in truth and directed toward the good of our neighbors. It needs Christians who understand that public responsibility is part of their calling and who are prepared to act accordingly. As André Schutten and Michael Wagner write in the Second Edition of A Christian Citizenship Guide:
“When it comes to political action, if not we, dear Christian citizen, then who? Who else would have the courage? Who else would know what to do? Who else would know how to fix the problem? We are a nation lost, without any sense of reality or morality. Canada needs a compass and a guide. The compass exists: it is the Word of God. The guides to read the compass are the faithful members of the church, scattered like leaven (Gal. 5:9) throughout all the institutions and spheres of Canadian culture and society and applying the truth and beauty and goodness of the Word of God in every sphere of life.”
Leaderboards will return in September, Lord willing. Until then, we celebrate those who stepped up and we invite others to join them. The competition may end each spring, but our calling as Christians does not.
Paul Lawton is ARPA’s Director of Grassroots Action, while Naomi Meerstra is ARPA’s Eastern Grassroots Coordinator. Pictures provided by ARPA Canada.